As industry observers, we closely track healthcare innovations that have transformative potential. The GLP-1 phenomenon sits firmly in this category—not just as another incremental advancement, but as a catalyst reshaping entire chronic disease and comorbidity landscapes across pharma, patient care, digital health, and beyond.
While mainstream conversation often pivots on Ozempic and Wegovy for celebrity weight loss, the real story is considerably deeper and more disruptive than what makes headlines.
What's Actually Happening with GLP-1s?
The United States has recently observed a modest but significant decrease in obesity rates for the first time in nearly a decade. While multiple factors are contributing to this shift, researchers have noted the potential influence of GLP-1 medications alongside pandemic-related behavior changes.
Despite their promise, several challenges exist: accessibility concerns, cost barriers, and troubling adherence patterns are creating significant implementation challenges. Recent industry reports indicate that weight loss medications now represent a substantial and growing portion of pharmaceutical expenditures, significantly impacting healthcare budgets.
The Pipeline Is Just Getting Started
While current market leaders Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly dominate headlines, the competitive landscape is poised for a dramatic expansion. Dozens of pharmaceutical companies are actively developing weight management agents across multiple mechanisms of action and formulations, with a significant portion still in early development phases.
The most exciting developments? Oral formulations. Several major companies are advancing novel oral GLP-1 receptor agonists through clinical trials, with promising early results. These oral options could fundamentally change the outlook on accessibility and adherence.
These Aren't Just Weight Loss Drugs Anymore
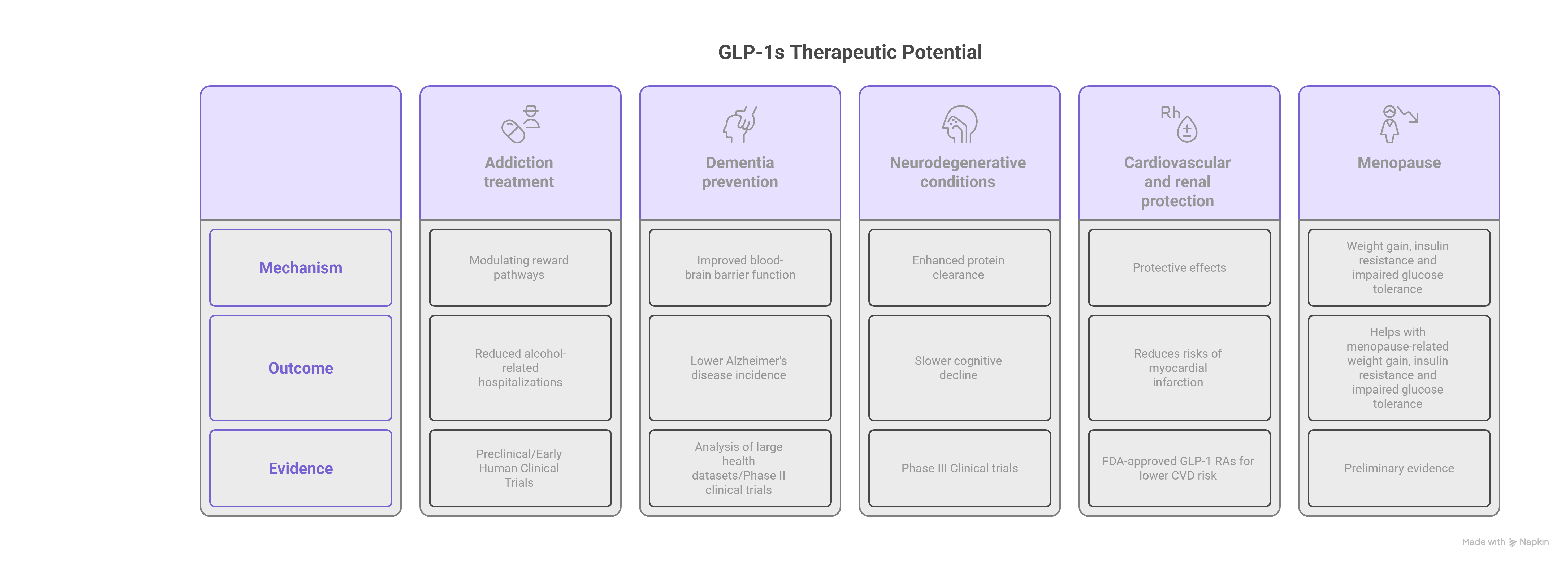
The therapeutic potential of GLP-1s is expanding far beyond obesity and diabetes into the world of comorbidities. A corpus of clinical evidence is being generated on new applications:
Pain management: GLP-1 receptor agonists show promise by inhibiting TRPV1 channels—key mediators of pain sensitivity. Preclinical studies demonstrate significant reductions in inflammatory and neuropathic pain without the hyperthermia associated with conventional pain medications, potentially offering a novel approach to chronic pain management.
Addiction treatment: Recent clinical evidence suggests GLP-1s may help treat substance use disorders by modulating reward pathways. Population studies show reduced alcohol-related hospitalizations with these medications, outperforming some traditional addiction treatments. With only two FDA-approved drugs for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), the repurposing of GLP-1s suddenly becomes a potential new source of treatment options.
Dementia prevention: Analysis of large health datasets reveals GLP-1 medications are associated with lower Alzheimer's disease incidence compared to other diabetes treatments—independent of glucose regulation. These neuroprotective effects appear linked to improved blood-brain barrier function, enhanced amyloid clearance, and reduced neuroinflammation.
Neurodegenerative conditions: Clinical trials examining semaglutide in Alzheimer's disease show preliminary evidence of slower cognitive decline, while studies in Parkinson's disease demonstrate improved motor function scores. GLP-1s appear to work through multiple mechanisms, including enhanced protein clearance and cerebrovascular protection.
Cardiovascular and renal protection: GLP-1 medications demonstrate protective effects for cardiovascular and renal health beyond their primary indications, reducing risks of myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, and diabetic kidney disease progression
Menupause: Preliminary evidence suggests GLP-1s may help with menopause-related weight gain, insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance - especially when combined with HRT - but more research is needed before becoming standard care.
Beyond these emerging applications, pharmaceutical innovation is now focusing more and more on combination therapies. Researchers are exploring how pairing GLP-1 medications with complementary agents—such as GIPR antagonists, glucagon receptor agonists, and amylin receptor agonists—might amplify therapeutic benefits across multiple conditions simultaneously. This approach reflects healthcare's broader evolution toward more sophisticated, multi-target interventions that maximize clinical outcomes while potentially improving cost-effectiveness and patient convenience.
The Digital Health & Compounding Landscape
The accessibility and affordability challenges surrounding approved GLP-1 drugs have sparked a significant market response: digital health companies entering the compounding space. Companies like Noom, Hims & Hers, and Ro have begun offering compounded versions of GLP-1 medications at substantially lower price points than branded alternatives, but are only permitted to do so by regulators during shortages..
This market evolution has triggered a series of notable developments:
Digital health companies have launched bold marketing initiatives—including prime-time advertising during major sporting events—directly challenging the traditional pharmaceutical pricing model
In response, manufacturers like Eli Lilly have introduced single-use vial options at reduced price points to compete with compounded alternatives
The FDA has taken regulatory action regarding compounding, including a February 2025 declaration on semaglutide shortage status that impacts compounding permissions
We're now seeing strategic alliances forming between digital health platforms and pharmaceutical manufacturers, suggesting a potential convergence rather than continued competition
Pharma Goes D2C
Perhaps most revolutionary is how GLP-1s have accelerated pharma's direct-to-consumer transformation. Recent direct-to-patient platforms from major pharmaceutical manufacturers represent a permanent shift in the healthcare landscape - creating improved transparency in pricing and distribution for patients, while enabling established pharmaceutical companies to compete more effectively with more agile digital health startups. This evolution is a departure from the traditional multi-layer distribution model that has characterized pharmaceutical delivery for decades, potentially reshaping patient access pathways and industry power dynamics for years to come.
The Big Questions Ahead
The GLP-1 story is just beginning. Key dynamics to watch include:
How will the 120+ pipeline candidates differentiate in an increasingly crowded market?
Will oral formulations solve the adherence crisis?
Can healthcare systems sustain the financial impact of broader GLP-1 adoption?
How will expanded therapeutic applications beyond weight loss reshape treatment paradigms?
What happens to the compounding market as FDA restrictions tighten?
Join the Conversation
This isn't just about weight loss pills—it's about rewiring the entire healthcare system from clinical pathways to payer strategies to market dynamics.
Want more insights on this transformative trend? Join HLTH experts Francesca Wuttke (Head of Insights & Advisory) and Tessy Huss (Director of Strategy) for "The GLP-1 disruption: what's next in the weight loss therapeutics race" webinar on 29th May at 12pm ET. They'll break down the future of care, access, and market dynamics in the GLP-1 space.
Free to attend. Insight-packed. Expert-led. Register here →

